Yana Kashilska*, Atanas Petkov**, Plumelina Micheva*, Atanas Batashki**, Zhivka Batashka ***
*Specialized Hospitals for Rehabilitation, National Complex EAD
** Department of Special Surgery, Medical University of Plovdiv
*** Medical College, Plovdiv
This article is a précis of an original article. PCNR would like to thank the publishers for their kind permission to publish this version.
Kashilska Y., Petkov A., Micheva P., Batashki A., Batashk Z. (2015): Improving the quality of life through effects of treatment with low intensity extremely low-frequency electrostatic field - DEEP OSCILLATION® in patients with breast cancer with secondary lymphoedema to patients treated with standard lymph equipment. Medicine. V(1), 381-387
ABSTRACT
Objective: To examine functional disorders in women with post breast surgery lymphoedema and to evaluate the therapeutic benefits of treatment with low intensity and extremely low frequency electrostatic fields using Deep Oscillation® and manual lymphatic drainage and a standard regimen of vacuum-assisted lymphatic drainage.
Methods: Twenty-one patients were divided into two randomised groups. The first group comprised 11 women who were treated with 10 sessions of manual lymphatic drainage with Deep Oscillation. The second group (control) comprised 10 women who were treated with standard lymphatic drainage only. Subjective assessment included pain and swelling; range of motion in the shoulder joint; movement of the neck, and an analysis of the volume of the chest using a 3D measuring system.
Results: At study start, patients had high scores for pain; swelling of the extremities; restricted movement in the shoulder joint; restriction in the movement of the spine in the neck portion. During the course of treatment pain reduced in intensity and shoulder joint movement increased in both groups. However, in the study group these were much greater.
Swelling only decreased in the Deep Oscillation group.
Conclusion: Manual lymph drainage with deep oscillation leads to a significant reduction in pain relief and reduction swelling in patients with lymphoedema compared with standard mechanical lymphatic drainage.
Keywords: breast cancer, pain, swelling, lymphatic drainage, low intensity and low frequency electrostatic fields
Breast lymphoedema
Goffmann et al [1] define breast lymphoedema as:
Swelling of the breast and formation of “orange peel” skin, combined with the sensation of heaviness and pain.
Rönkä et al. [2] in a study of 160 patients, found breast swelling in 34% of the patients, orange skin in 3.8%, and sensitivity to palpation of the breast in 59%. They noted that the risk of developing lymphoedema correlates to the number of lymph-nodes removed.
Patients with breast lymphoedema experience chronic pain of medium to high intensity and associated discomfort, which leads to deterioration in quality of life. Commonly, lymphoedema is diagnosed in the arm of the affected breast, whereas breast lymhoedema is rarely discussed or considered. And while limb lymphoedema of the arm can be quantitatively measured, the only objective way to ascertain breast lymphoedema is examining the altered thickness of the skin flap. This parameter, however, is poorly reproducible and unreliable.
The Specialised Hospital for Rehabilitation provides a Physical and Rehabilitation Program for the management of breast lymphoedema post-breast cancer surgery. This 10-day programme is undertaken by physicians of physical and rehabilitation medicine, physiotherapists, kinesiotherapists, rehabilitation therapists, occupational therapists, oncologists, dieticians, clinical psychologists, and art-therapists.
Study
The objectives of this study were:
- To identify functional disorders in women with secondary lymphoedema after surgical treatment
- To evaluate the benefits of treatment with low intensity and extremely low frequency electrostatic fields reproduced by Deep Oscillation® with a program of standard vacuum-machine lymph drainage, compared to a programme of standard vacuum-machine lymph drainage (Lymphastim, BTL), applied to the arm lateral to the affected breast
Inclusion criteria
- Patients who underwent breast sparing surgery no earlier than three months before, had completed active treatment (20 days after radiotherapy, or 10 days after chemotherapy in succession), were on adjuvant therapy
- TNM classification pT1 pN0 M0; pT2 pN0 M0; pT4 pN0 M0, with lymph node dissection L0, without distant metastases, i.e. in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd A stage
Exclusion criteria
- Patients who had received Deep Oscillation® treatment within 3 months prior to study
- Patients with acute inflammation, acute thrombosis, cardiovascular disease, electronic implant, pregnancy, or subjective sensitivity to electrical fields
Parameters assessed (pre and post study) included:
- Pain (using VAS)
- Lymphatic drainage analysis of the upper limb
- Kinesiological analysis of the upper limb for the range of motion in the shoulder joint, and the neck (reference limits of normal movement: lateral flexion at 45°, rotation 60°, anteflexion 40°, retroflexion 30°)
- 3D measurement of the volume of the operated breast with callipers
- Onco-haematological analysis
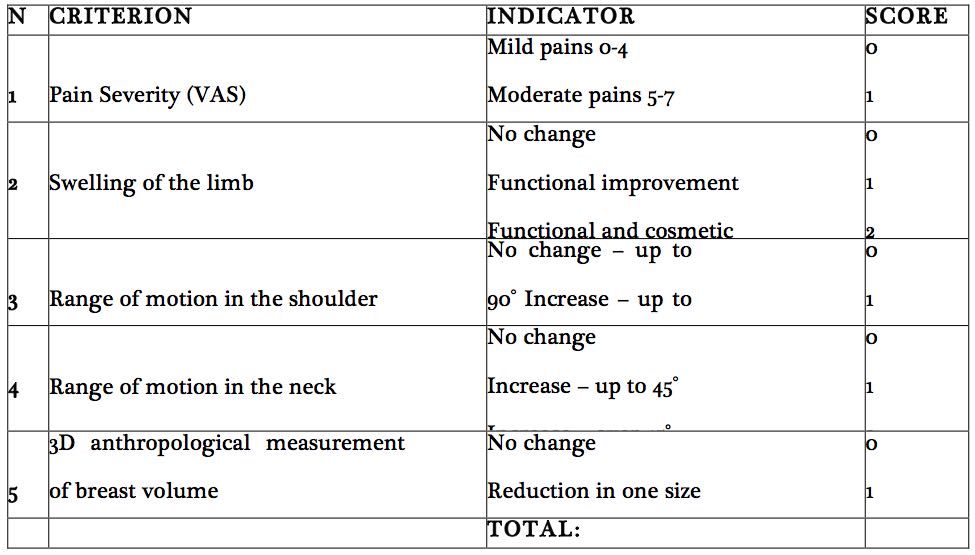
- Quality of life: pre-and post result were recorded in Table 1 based on pain, swelling, range of motion and swelling. Criterion were scaled; 0, 1 or 2 points; a score between 0 and 3 points indicates no improvement in the quality of life, a score between 4 and 7 indicates an ‘good’ improvement in the quality of life, and between 8 and 10 indicates ‘very good’ improvement in quality of life.
Method
Twenty-one patients were enrolled into the study and were assigned to either the study group (11 patients) or control group (10 patients). Both groups received therapy in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Results
- Twenty-one women were included in the study. Their ages ranged between 29 and 61 years, average 45 years old
- Nine patients had surgery on the left breast, 12 patients had right breast surgery
- All patients had undergone adjuvant radiotherapy 4 to 5 months prior to study
- Pain in all patients in both groups was 4.9 on the visual analogue scale VAS
- 11 patients were placed in the study group, 10 in the control. 100% of patients in the study group saw improvements in all parameters assessed: 2 patients (18.5%) saw a 1 cm reduction in the circumference of the affected limb with associated functional improvement, the remaining nine (81.5%) saw a reduction of 1.5 to 3 cm, thus proportionality in the both limbs has been achieved – functionally and cosmetically.
- In the study group, an increase in the range of motion in the affected shoulder joint of up to 50% was observed in 2 patients (18.5 %) and over 50% in the remaining 9 (81.5%), which led to reference values of the motion in the joint
- All patients had reduced neck mobility at study start; movement was improved in the test group, with an associated reduction in pain
- A reduction in swelling of the breast was seen in the study group only
After analysing the results achieved using the TLQ-scale (table 1), 1 (0.9%) patient in the study group demonstrated a ‘good’ improvement in her quality of life; the remaining 10 (99.1%) showed ‘very good’ improvement. In the control group, 3 (30%) patients demonstrated a ‘good’ improvement, with the remaining 7 (70%) indicating a ‘very good’ improvement. We attribute these differences to the change in the volume of breast lymphoedema in the study group.
Discussion
The Psychosocial Rehabilitation Program provided at the Specialised Hospital for Rehabilitation with by a range of specialist practitioners aims to ameliorate the negative effects of the chemo/ radiotherapy, improve the physical movement of the affected upper limb, improve general physical activity, and the overall condition of the body.
Deep Oscillation® applies a low-intensity intermittent electrostatic field (U = 100-400V; I = 150μA) and extremely low frequency (30-200Hz, biphasic rectangular) to the affected area. The electrostatic field attracts and releases the tissue, resulting in deep, resonant vibrations (Fickling 2014). The deep and lasting vibrations caused by the electrostatic low intensity field act upon the tissue and the accumulated toxins and sub-products in the extracellular space. The electrostatic field changes the polarity of the cell membrane, making them open and release the free radicals and metabolic sub-products accumulated in the cell cytoplasm of the cell into the extracellular space, and then into the lymph system.
The patient and the therapist are connected to the Deep Oscillation® device, serving as a voltage source of high internal resistance, a special glove serves as an insulator. The impulse of the voltage causes an electrostatic force of attraction of the tissues and leads to a higher frictional force while the swelling is massaged.
CONCLUSION
Deep Oscillation® with a program of lymph drainage improved the quality of life in all study group patients.
While this technology is innovative in our country, the team will continue to work in this direction while we will gradually cover larger groups of patients while safe keeping their health and in the name of the better and modern treatment.
We express our gratitude to Acad. Dr Damyan Damyanov, MD and Prof. Dr. Elena Ilieva, MD without the efforts of which hundreds of women operated for breast cancer could not receive an adequate postoperative rehabilitation treatment.


























